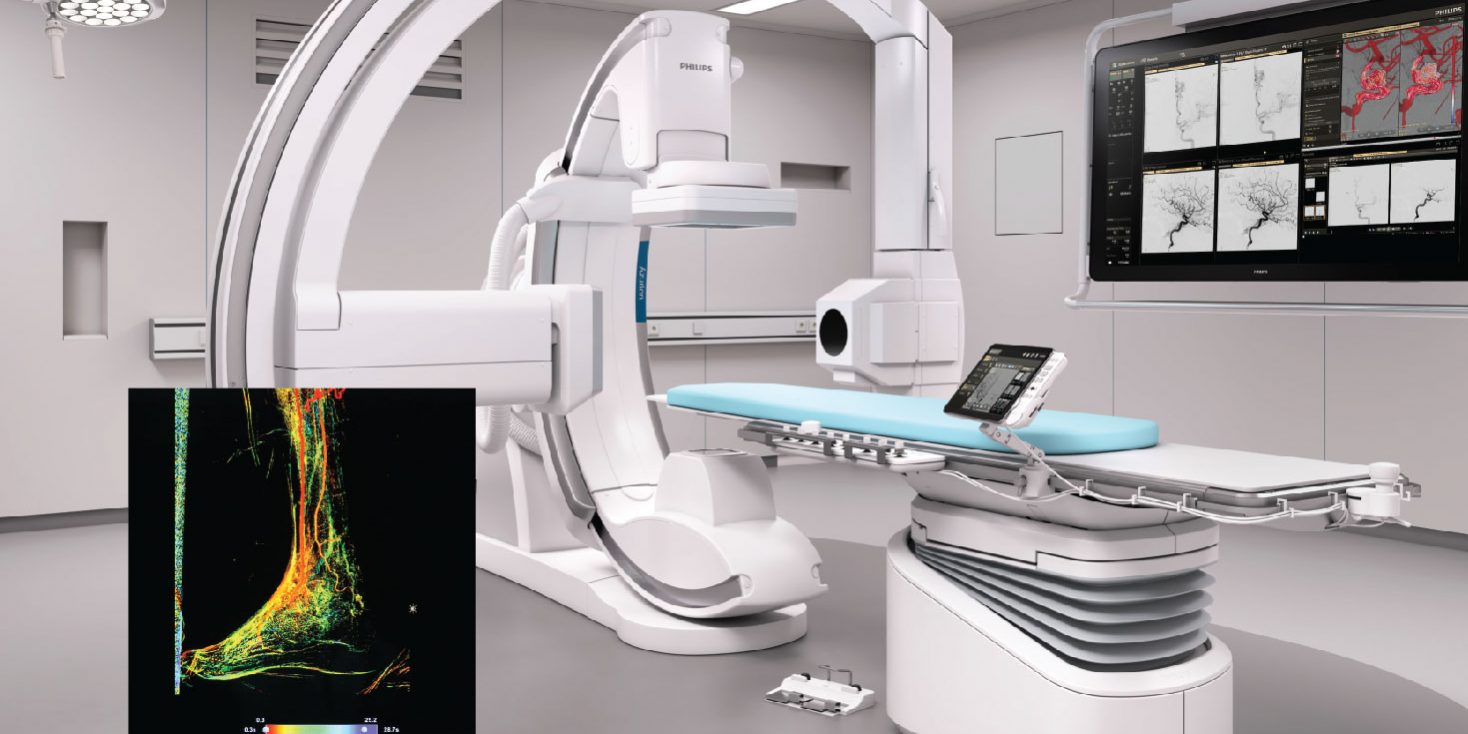
Most Advanced Biplane Catheterisation Laboratory in South Asia supports clinicians in vascular procedures.
Prolonged pain in lower limbs and difficulty walking may sometimes be due to peripheral arterial disease (PAD), caused by narrowing or blockage of the arteries. A procedure has to be done to widen or remove the blockage in the arteries. This procedure is known as Peripheral Angioplasty.
During the Peripheral Angioplasty procedure the catheter is inserted into the artery and passed through the block or narrowed area. A special balloon at the end of the catheter is put into the narrowing or the block and inflated and deflated several times to increase the blood flow of the blood vessel. A stent which is a metal mesh may be placed across the affected area to keep the artery open.
Before the procedure, local anaesthesia is injected in to the groin area. Afterwards a small cut is made in the skin and the needle inserted through the groin arteries. The thin tube is then guided into the area using image guided therapy to the affected area. A clear X-ray dye called Contrast is injected through the catheter allowing blood vessels and any narrowed areas or blockage in the artery to be seen clearly for treatment. With Philips Azurion Image Guided Therapy the amount of dye that has to be used is less and is therefore safer for patient.
Powerful performance of the most advanced X-ray tube in the image guidance system facilitates enhanced detection. New interventional tools built into it such as VasoCT and AneurysmFlow are a first in South Asia and provide more accurate navigation inside vessels and better guides the precise device placement procedures. In stent procedures this system aids the right sized stent to be placed in the right location. Special peripheral perfusion imaging is available for interventions to assess pre and post interventional flow dynamics and perfusion.
Durdans Hospital Biplane Catheterisation Laboratory is the most advanced in South Asia that can be used towards superior vascular interventions along with cardiac, neuroradiology and oncology interventions. Compared to a single plane the biplane captures image data from detectors on two axes thus the image is obtained faster.